Zymolyase-20T / Zymolyase-100T
Zymolyase®, produced by a submerged culture of Arthrobacter luteus(1), has strong lytic activity against living yeast cell walls(2),(3) to produce protoplast or spheroplast of various strains of yeast cells. An essential enzyme for the lytic activity of Zymolyase® is β-1,3-glucan laminaripentaohydrolase. It hydrolyzes linear glucose polymers with β-1,3-linkages and releases specifically laminaripentaose as the main and minimum product unit(4), (5), (10), (11).
Product Information
There are two preparations of Zymolyase®, Zymolyase®-20T and Zymolyase®-100T, having lytic activity of 20,000 units/g and 100,000 units/g respectively. Zymolyase®-20T is ammonium sulfate precipitate while Zymolyase®-100T is a further purified preparation by affinity chromatography(9). Lytic activity varies depending on yeast strain, growth stage of yeast, or cultural conditions(6-8). Further informations related to Zymolyase® can be obtained in the reference section below(12-16).
Product Information
| Product Name | Zymolyase®-20T | Zymolyase®-100T | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Form | Lyophilized Powder | ||
| Purification | Ammonium Sulfate Precipitation | Affinity Chromatography | |
| Activity | 20,000 units/g | 100,000 unites/g | |
| Essential enzyme | β-1,3-glucan laminaripentaohydrolase | ||
| Other activities contained (※1) |
β-1,3-glucanase | approx. 1.5 x 106 units/g | approx. 1.0 x 107 units/g |
| protease | approx. 1.0 x 104 units/g | approx. 1.7 x 104 units/g | |
| mannanase | approx. 1.0 x 106 units/g | approx. 6.0 x 104 units/g | |
| Contaminants | Amylase, Xylanase, Phosphatase |
Trace amount | Non detectable |
| Optimum pH and Temp. | pH7.5, 35°C (for lysis of viable yeast cells) pH6.5, 45°C (for hydrolysis of yeast glucan) |
||
| Stability | 2°C | No loss of activity was found after storage for 1 year | |
| Heat stability | 30°C | 70% of the lytic activity is lost after storage for 3 months | |
| 90% of the lytic activity is lost after storage for 3 months | |||
| 60°C | Lytic activity is lost on incubation for 5 minutes | ||
| Specificity (Lytic Spectrum) | Ashbya, Candida, Debaryomyces, Eremothecium, Endomyces, Hansenula, Hanseniaspora, Kloeckera, kluyveromyces, Lipomyces, Metschnikowia, Pichia, Pullularia, Torulopsis, Saccharomyces, Saccharomycopsis, Saccharomycodes, Schwanniomyces, etc. | ||
(※1) See reference, Kitamura, K., Kaneko, T., Yamamoto, Y., J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol., 18, 57 (1972) as to the definition of each enzyme units.
Unit Definition
One unit of lytic activity is defined as that amount which indicates 30% of decrease in absorbance at 800 nm(A800) of the reaction mixture under the following condition.
Reaction Mixture
| Enzyme solution |
1 ml (0.05-0.1 mg/ml for Zymolyase®-20T) 1 ml (0.012-0.024 mg/ml for Zymolyase®-100T) |
|
| Brewer's yeast cell suspension | 3 ml (2 mg/ml) | |
| 1/15M Phosphate buffer | 5 ml (pH7.5) | |
| Distilled water | 1 ml | |
After incubation for 2 hours at 25°C with gentle shaking, A800 of the mixture is determined. When 60% of A800 decrease, equivalent to 2 units, is observed in the reaction system, the brewer’s yeast cells are completely lysed, namely 1 unit of Zymolyase® lyses 3 mg dry weight of brewer’s yeast.
Applications
Electron microscopical photo of yeast cell
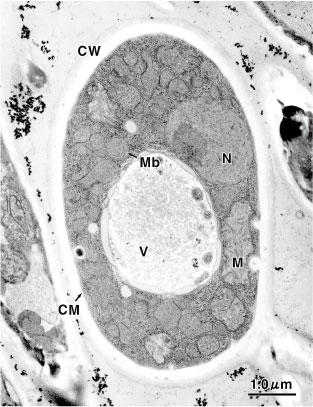
Electron microscopical photo of yeast cell
(Candida tropicals)
CW: Cell Wall
CM: Cell Membrane
M: Mitochondria
Mb: Microbody
N: Nucleus
V: Vacuole
↓
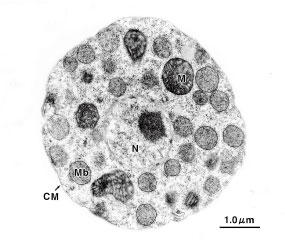
Yeast cell(Candida tropicalis)
after Zymolyase® treatment.
(Data courtesy of Professor Masako Osumi, Nippon Women's University)
Protocols
- Zymolyase®-20T
 (PDF 86 KB)
(PDF 86 KB) - Zymolyase®-100T
 (PDF 86 KB)
(PDF 86 KB)
Preparation of 1/15 M Phosphate Buffer (1L of pH 7.5 buffer)
- Dissolve 19.1 g of di-sodium hydrogenphosphate 12-hydrate in distilled water to make an 800 mL solution.
- Dissolve 1.814 g of potassium dihydrogenphosphate in distilled water to make a 200 mL solution.
- Mix the two solutions.
The below phosphate buffers (pH 7.5) have been tested for compatibility.
|
Buffer |
Concentration |
Yeast Lytic activity (unit/g) |
|---|---|---|
|
Potassium/Sodium Phosphate Buffer |
1/15 M |
21,000 |
|
Potassium Phosphate Buffer |
5 mM |
20,300 |
|
10 mM |
21,400 |
|
|
50 mM |
21,000 |
|
|
Sodium Phosphate Buffer |
5 mM |
20,500 |
|
10 mM |
21,200 |
|
|
50 mM |
21,200 |
References
- K Takagi et al.: Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin?64.5 (2016): 432-438
- S Ikushiro et al.: Molecular pharmaceutics(2016)
- M Schuler et al.: Journal of Biological Chemistry(2016): jbc-M116
- E Tanaka et al.: Plant Pathology (2016)
- S Yamamoto et al: Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications (2016)
- Y Ootsubo et al.: Bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry80.4 (2016): 748-760
- Y Morimoto et al.: Molecular microbiology 95.4 (2015): 706-722
- M Murai et al.: Biochemistry 53.24 (2014)
- M Asaoka et al.: Journal of biochemistry156.6 (2014)
- Herrero Enrique, Sanz Pascual. Sentandreu Rafael: J. Gen. Microbiol., 133 (10), 2895 (1987)
- Iijima Y., Yanagi S. O.: Agric. Biol. Chem., 50 (7), 1855 (1986)
- Shibata Nobuyuki, Kobayashi Hidemitsu, tojo Menehiro, Suzuki Shigeo: Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 251(2), 697 (1986)
- Iizuka Masaru, Torii Yasuhiko, Yamamoto Takehiko: Agric. Biol. Chem., 47 (12), 2267 (1983)
- Calza R. E., Schroeder A. L.: J. Gen. Microbiol., 129, 413 (1983)
- Kitamura, K.: Agric. Biol. Chem., 46, 2093 (1982)
- Kitamura, K.: Agric. Biol. Chem., 46, 963 (1982)
- Katamura, K.: J. Ferment. Technol., 60, 257 (1982)
- Katamura, K. and Tanabe, K.: Agric, Biol. Chem., 46, 553 (1982)
- Kitamura, K. and Yamamoto,.: Agric. Biol. Chem., 45, 1761 (1981)
- Kitamura, K., Kaneko, T. and Yamamoto, Y.: J. Gen Appl. Microbiol., 20, 323 (1974)
- Kaneko, T., Kitamura, K. and Yamamoto, Y.: Agric. Biol. Chem., 37, 2295 (1973)
Downloads
Zymolyase®-20T and Zymolyase®-100T![]() (PDF 637 KB)
(PDF 637 KB)