Molecular Targeting Technologies社 ホスファチジルセリン検出プローブ

PSVue™ reagents are a family of fluorescent probes containing a bis(zinc2+dipicolylamine) group (Zn-DPA), a motif that has been found to bind with high affinity to surfaces enriched with anionic phospholipids, especially phosphatidylserine (PS) exposed on cell membranes. The fluorescent part of the probe is a reporter element that provides a means of detecting the probe once it is bound to the membrane of interest.
Key Features of PSVue™ Probes:
- Bind to a variety of cell types which have negatively charged phospholipids exposed on their membranes including apoptotic cells [1], necrotic cells [2], Gram + ve and Gram ? ve bacteria [3-5], activated cells, tumor vascular endothelial cells, viruses, etc.
- Available in a range of detection wavelengths from long-UV to near infrared.
- Suitable for in vitro and in vivo use.
- Suitable for high-throughput screening assays.
- Bind to the same PS site as annexin-V.
Advantages of PSVue™ over Fluorescent Annexin-V:
- Binding kinetics are fast; annexin-V binding is slow [6,7]
- Binding is Ca2+ independent; means no artifacts due to activation of nonspecific membrane scramblases by Ca2+ [8].
- Cheap compared to most annexin-V fluorescent analogs
- Apoptosis can be detected under a wide variety of conditions(e.g. in presence of 10% serum, temps from 4 to 37oC) [8].
- Can provide more intense labeling due to their much smaller size (i.e. >10 PSVue™ molecules can bind to the same area as 1 annexin V molecule) [9].
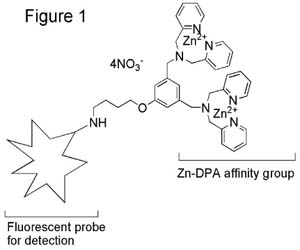
General Structure of PSVue™ Probes (Figure 1)
In Vitro Studies:
Several in vitro studies have shown that PSVue compounds stain the same apoptotic cells as fluorescently labeled annexin-V indicating that they are excellent small molecule mimics of annexin-V. An example using PSVue 794 is shown in Figure 2 [2].
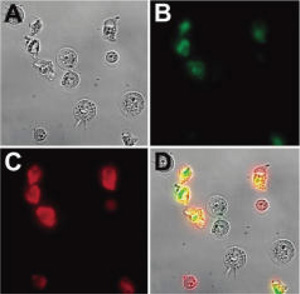
Figure 2. Micrographs (60X magnification) of Jurkat cells, treated with cytotoxic camptothecin (10 µM) for 3.5 h and stained simultaneously with Annexin V conjugated dye (competitor A), and PSVue 794 (10 µM). Brightfield image of the entire field of cells (A); cells stained with Annexin V conjugated dye (competitor A) (B); cells stained with PSVue 794 (C); overlay of images A, B, and C (D). No staining of healthy cells was observed in the absence of camptothecin. (Images courtesy of Dr. Bradley Smith of University of Notre Dame)
Proposed Model of Membrane Binding [8,9]:
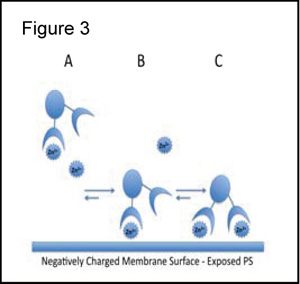
Figure 3 illustrates the 3 component assembly process that results in high affinity association of PSVue with PS-rich membranes. Under physiologic concentrations of Zn2+ the predominant coordination complex is the mono-zinc species (species A). The binding of species A to the anionic PS exposed membrane (species B) would promote the binding of the second Zn2+ with subsequent binding to the membrane forming a bivalently-bound species C. PSVue reagents are selective for membrane phosphates and do not stain the cytosol.
Selected In Vivo Studies:
The in vivo images below show that in animal models of prostate cancer (Figure 4) [2], mammary cancer (Figure 5) [2] and bacterial infections (S. aureus) (Figure 6) [4], PSVue™ targeted to the disease site.
Figure 4. X-ray and fluorescence overlay image of a rat prostate tumor model at 24 h postinjection of PSVue 794 (4.0 mg/kg) shows clear evidence of selective accumulation in the tumor. The image was acquired at a 190 mm field of view. (Image courtesy of Dr. Bradley Smith of University of Notre Dame)
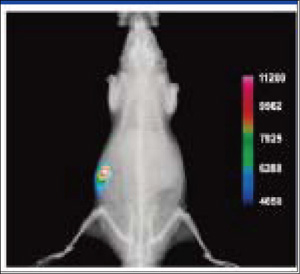
Figure 5. Representative overlay image of a nude mouse with an EMT-6 mammary tumor. Brightfield and fluorescence intensity images were acquired 24h following injection of PSVue 794 and show clear evidence of selective accumulation in the tumor. The image was taken at a 80 mm field of view. (Image courtesy of Dr. Bradley Smith of University of Notre Dame)
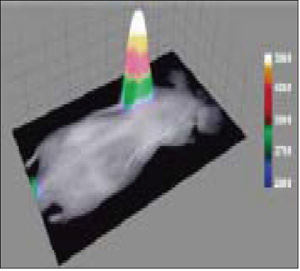
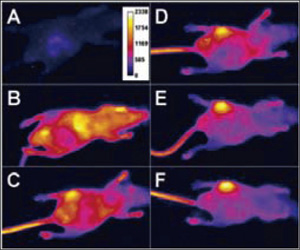
Figure 6. Optical image of a mouse with a S. aureus infection in the left rear thigh muscle. Images were acquired before (A), and immediately following (B), iv injection of PSVue 794 and at 6h (C), 12h (D), 18 h (E) and 21 h (F). (Images courtesy of Dr. Bradley Smith of University of Notre Dame)
References:
- Hanshaw RG, Lakshmi C, Lambert TN, Johnson JR and Smith BD. Fluorescent detection of apoptotic cells by using zinc coordination complexes with a selective affinity for membranes surfaces enriched with phosphatidylserine. ChemBioChem, 2005, 6, 2214-2220.
- Smith BA, Akers WJ, Leevy WM, Lampkins AJ, Xiao S, Wolter W, Suckow MA, Achilefu S and Smith BD. Optical imaging of mammary and prostrate tumors in living animals using a synthetic near infrared zinc(II)-dipicolylamine probe for anionic cell surfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132 (1), 67-69.
- Leevy, WM; Johnson, JR.; Lakshmi, C.; Morris, J.; Marquez, M.; Smith, BD. Selective recognition of bacterial membranes by zinc(II)-coordination complexes. Chem. Commun. 2006, 595-1597.
- Leevy WM, Gammon, ST, Jiang H, Johnson JR, Maxwell DJ, Marquez M, Piwinica-Worms D and Smith BD. Optical imaging of bacterial infection in living mice using a fluorescent near-infrared molecular probe. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 16476-16477.
- leevy WM, Gammon ST, Johnson JR, Johnson JR, Lampkins AJ, Jiang H, Marquez M, Piwinica-Worms D and Smith BD. Noninvasive optical imaging of Straphylococcus aureus bacterial infection in living mice using a bis-dipicolylamine-zinc (II) affinity group conjugated to a near infrared fluorophore. Bioconj. Chem. 2008, 19, 686-692
- DiVittorio KM, Johnson JR, Johansson E, Reynolds AJ, Jolliffe KA and Smith BD. Synthetic peptides with selective affinity for apoptotic cells. Org. Biomol. Chem., 2006, 4, 1966-1976.
- Koulov AV, Stucker KA, Lakshmi C, Robinson JP and Smith BD. Detection of apoptotic cells using a synthetic fluorescent sensor for membrane surfaces that contain phosphatidylserine. Cell Death and Differentiation, 2003, 10, 1357-1359
- Hanshaw RG and Smith BD. New reagents for phosphatidylserine recognition and detection of apoptosis. Bioorg. & Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 5035-5042
- Koulov AV, Hanshaw RG, Stucker KA, Lakshmi C and Smith BD. Biophysical studies of a synthetic mimic of the apoptosis-detecting protein annexin V. Israel. J of Chem., 2005, 45, 373-379.
- Leevy WM, Lambert TN, Johnson JR, Morris J and Smith BD. Quantum dot probes for bacteria distinguish Escherichia coli mutants and permit in vivo imaging. Chem. Commun., 2008, 2331-2333.
| Catalog No. | Product Name | Structure | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| P-1001 | PSVue™ 794 | 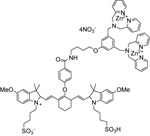 |
The PSVue™794 (formerly PSS-794) reagent kit contains components to provide ~ 0.68 mL of a 1 mM solution of PSVue™794 in aqueous solution. The compound exhibits absorbance and fluorescence excitation maximum at 794 nm and emission maximum at 810 nm. The labeling vehicle provided with the kit (Diluent X) is designed to maximize dye solubility and is suitable for in vitro and in vivo use. |
| P-1002 | PSVue™ 380 | 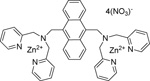 |
The PSVue™380 (formerly PSS-380) reagent kit contains components to provide ~ 0.40 mL of a 2 mM solution of PSVue™380. The compound has an absorbance max at 380 nm and a fluorescence emission max at 440 nm. |
| P-1003 | PSVue™ 480 | 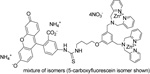 |
The PSVue™480 (formerly PSS-480) reagent kit contains components to provide ~0.5 mL of a 1 mM solution of PSVue™480. The compound has an absorbance max at 480 nm and an fluorescence emission max at 519 nm |
| P-1004 | PSVue™ Biotin | 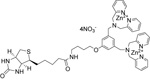 |
Vial contains 1mg of solid. PSVue™ biotin can be complexed with streptavidin-coated quantum dots (not provided) for in vivo and in vitro use. Procedures to formulate PSVue™biotin and prepare the PSVue™ biotin-streptavidin -coated quantum dot complex are provided. |
| P-1005 | PSVue™ 550 | 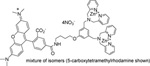 |
The PSVue™550 reagent kit contains components to provide ~0.5 mL of a 1 mM solution of PSVue™550. The compound has an absorbance max at 553 nm and an fluorescence emission max at 615 nm |
PSVue™ is a trademark of Molecular Targeting Technologies, Inc. PSVue™ products are sold under an exclusive license from the University of Notre Dame. US Patent # 7,179,616 and others pending.
Fount of Information は、新商品、新規取扱メーカーなどの情報をいち早く紹介するコンテンツです。情報発信のスピードを重視しているコンテンツのため、現時点で法規制や取り扱いを確認できていない商品、定価を設定できていない商品があります。ご要望やご照会を受けた商品について、法令整備や在庫の充実を図ります。