OriGene社 Alzheimer's Disease: Biomarkers and Latest discoveries
| この製品に関するご意見・ご照会・お問合せはこちら
 Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disorder characterized by dementia that generally initiates with a subtle failure of memory, progressing over the years to an incapacitating level. It is characterized by extracellular amyloid plaques and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles, resulting in neuronal dysfunction and cell death. Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disorder characterized by dementia that generally initiates with a subtle failure of memory, progressing over the years to an incapacitating level. It is characterized by extracellular amyloid plaques and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles, resulting in neuronal dysfunction and cell death.
|
|
The two most popular targets in AD research are
|
|
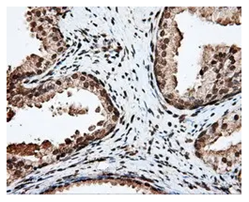
Beta-Amyloid
The generation of the Beta-Amyloid (Aβ) peptide through the proteolytic processing of the Amyloid precursor protein (APP) is a central event in the pathogenesis of AD. Extracellular accumulation of Aβ leads to forming aggregates, fibrils, and eventually, amyloid deposits called neuritic plaques, a hallmark of AD.
Clones | Antibodies | Proteins | RNAi
|
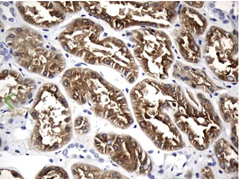 |
MAPT/Tau
Tau is a microtubule-associated protein (MAP) involved in microtubule stabilization. In Alzheimer's, tau becomes hyperphosphorylated and detaches from microtubules. Phosphorylated tau then aggregates to form paired helical filaments (PHFs) and neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs)
Clones | Antibodies | Proteins | RNAi
|
|
Latest Discoveries in AD research
Scientists developed an antibody-based blood test that would detect brain-derived tau to predict deposits in the brain |
|
Other related markers
|
Fount of Information は、新商品、新規取扱メーカーなどの情報をいち早く紹介するコンテンツです。情報発信のスピードを重視しているコンテンツのため、現時点で法規制や取り扱いを確認できていない商品、定価を設定できていない商品があります。ご要望やご照会を受けた商品について、法令整備や在庫の充実を図ります。