Poor peak shape
T1. Poor peak shape
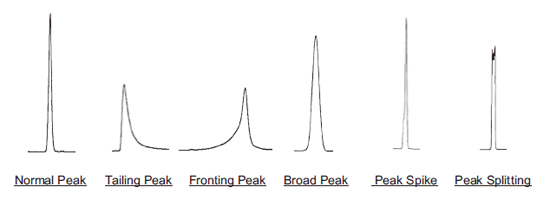
| Symptom | Cause | Solution | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Particular sample is tailing | Undesirable ion exchange interaction between basic compounds and packing material. | Use a column with fewer residual silanols (3C18- EB or 5C18-MS-II), or add 0.1-1% acid to mobile phase. | |
| Undesirable coordinate interaction between metal coordination compound and packing material. | Add 5 mmol/l of di-sodium dihydrogen ethylenediaminetetraacetate dihydrate (EDTA・2Na) to mobile phase. | ||
| Undesirable hydrogen bonding interaction between sample and packing material. | Change the organic solvent (e.g., acetonitrile to methanol). | ||
| All samples are tailing | Voids in packing material or column deterioration. | Replace the column. | |
| (If the tailing does not improve after replacing the column) Sample is dispersing inside the column. | Reduce dead volume (refer to Q25 for more information on dead volume). | ||
| Fronting | Injection of large volume of sample solvent that is significantly different in elution properties or pH compared to mobile phase. | Dissolve sample in mobile phase. If the sample does not dissolve, dissolve in a soluble solvent first, then dilute with mobile phase. | |
| Reduce injection volume to 1/2-1/10. Caution: Spikes or peak broadening may also occur. |
|||
| Broad peaks (1) Sample has high molecular weight (MW: 2,000 or greater). | Proteins with high molecular weight cannot access pores of packing material. | Use wide pore (pore size: 300Å) column for reversed phase chromatography, Protein-R. Please see web or catalog for more information. | |
| Sample volume is too large. | Reduce injection volume to 1/2-1/10. Caution: Tailing peaks may also occur. |
||
| If a particular sample has a broad peak, the compound may be adsorbed to the packing material. | Use Protein-R for a high recovery rate. Please see web or catalog for more information. | ||
| If all samples have broad peaks, the column may have deteriorated. | Replace the column. | ||
| Concentration of ammonium sulfate in sample solution is too low on hydrophobic chromatography (HIC). | Adjust concentration of ammonium sulfate to 1 mol/l or greater. | ||
| Broad peaks (2) Sample has low molecular weight (MW: 2,000 or less). | Sample volume is too large. | Reduce sample amount from 1/2 to 1/10. Caution: Tailing peaks may occur instead of broad peaks. |
|
| If a particular sample has a broad peak, the compound may be adsorbed to the packing material. | Replace with a column that has a different packing material. (3C18-EB and 5C18-MS-II are recommended for basic samples. ) |
||
| If all samples have broad peaks, the column may have deteriorated. | Replace the column. | ||
| Peak spikes or peak splitting occur for certain samples. | More than 2 samples are contained in the peak, and slightly separated. | Find the conditions that separate the two samples. | |
| Mobile phase and sample solvent are significantly different in their separation properties. | Dissolve sample in mobile phase. If sample does not dissolve, dissolve sample in soluble solvent, then dilute with the mobile phase. | ||
| Reduce injection volume to 1/2 to 1/10. | |||
| Mixed dissociated and non-dissociated ionic sample. | Adjust pH of mobile phase to pKa ±2 or more of the ionic sample. | ||
| Peak spikes or peak splitting occur for all samples | Mobile phase and sample solvent are significantly different in their separation properties. | Dissolve sample in mobile phase. If sample does not dissolve, dissolve sample in soluble solvent, then dilute with the mobile phase. | |
| Reduce injection volume to 1/2 to 1/10. | |||
| The column may have deteriorated. | Replace the column. | ||
T2. Ghost peaks
| Separation Mode | Cause | Solution | |
|---|---|---|---|
| <Reversed Phase Chromatography> Gradient elution |
Peaks from water impurities | Use new HPLC-grade distilled water. | |
| Use a pre-column. Please refer to Technical Information, Baseline Noise in Gradient Elution (PDF 600KB) | |||
| <Reversed Phase Chromatography> Protein samples |
Sample may be adsorb to the column, and elute on the next analysis. | Wash column, Please refer to Q3 for more information on washing methods. | |
| COSMOSIL Protein-R, which has high recovery rate for protein separations, is recommended. | |||
| <All Separation Modes> Sample solvent and mobile phase are significantly different. | Sample solvent has peaks. | Dissolve sample in mobile phase. If sample does not dissolve, dissolve sample in a soluble solvent, then dilute with the mobile phase. | |
| <All Separation Modes> Peaks in blank analysis (Peak area decreases with each injection.) |
Injector is contaminated. | Wash by injecting with a syringe 20 ml of solvent (e.g., methanol) that can dissolve the contaminants. | |
| Micro-syringe is contaminated. | Wash with solvent (e.g., methanol, chloroform or water) to dissolve the pollutants. Ultrasonic cleaning is effective. | ||
| Others | Contamination or deterioration of samples | Prepare the sample again. | |
| Stabilizers in the mobile phase | Use HPLC-grade solvent without stabilizers. | ||